1
/
of
5
Perpetua.life
NAD+ NMN Liposomal Anti Aging Supplement Complex AEON with Nicotinamide DUO™
NAD+ NMN Liposomal Anti Aging Supplement Complex AEON with Nicotinamide DUO™
Regular price
$59.00 USD
Regular price
$79.00 USD
Sale price
$59.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
"Amazing"
Rated 4.4/5 on

DESCRIPTION:
AEON™ Black & White is the World’s best anti-aging supplement bundle and the only one that combines powerful NAD+ precursors in a full spectrum 20-compound liposomal complex.
Take AEON Black in the AM to experience an all day energy boost and enhanced sense of well-being.
Follow that up by taking AEON White in the evening, before bed, to experience a deep and reinvigorating nights sleep.

Our formula is bound to a Liposomal Delivery Matrix that increases the absorption of each compound by 200-300% (source). SO LESS IS MORE!
AEON is free of preservatives, additives, gluten, animal derived ingredients, and has 0 calories. It's made in the USA, and rigorously tested by 3rd party labs for both potency, AND heavy metals to ensure you receive a premium product each, and every time (latest rest).
*This products formulation is kept up to date with the latest longevity research so the formula/ingredients may change slightly over time.
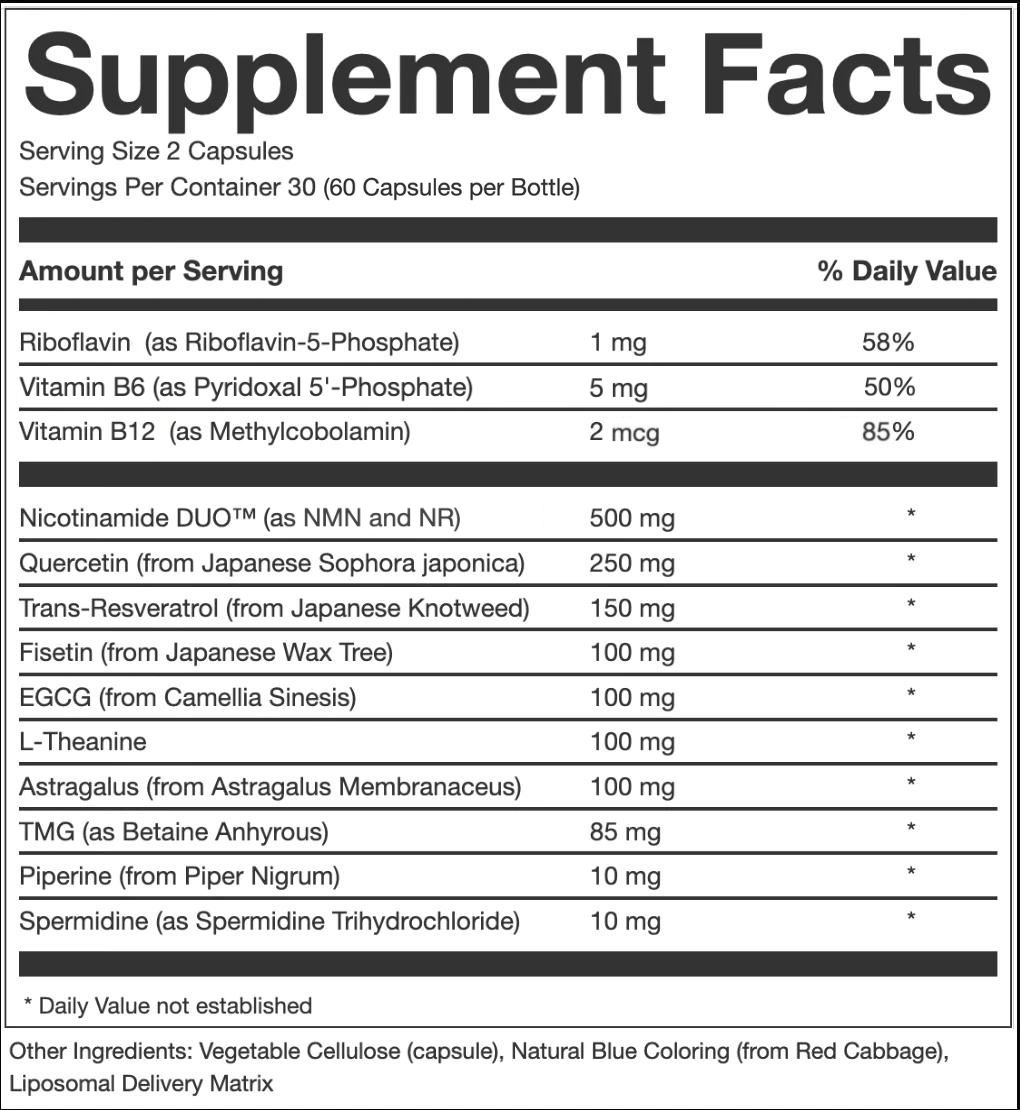
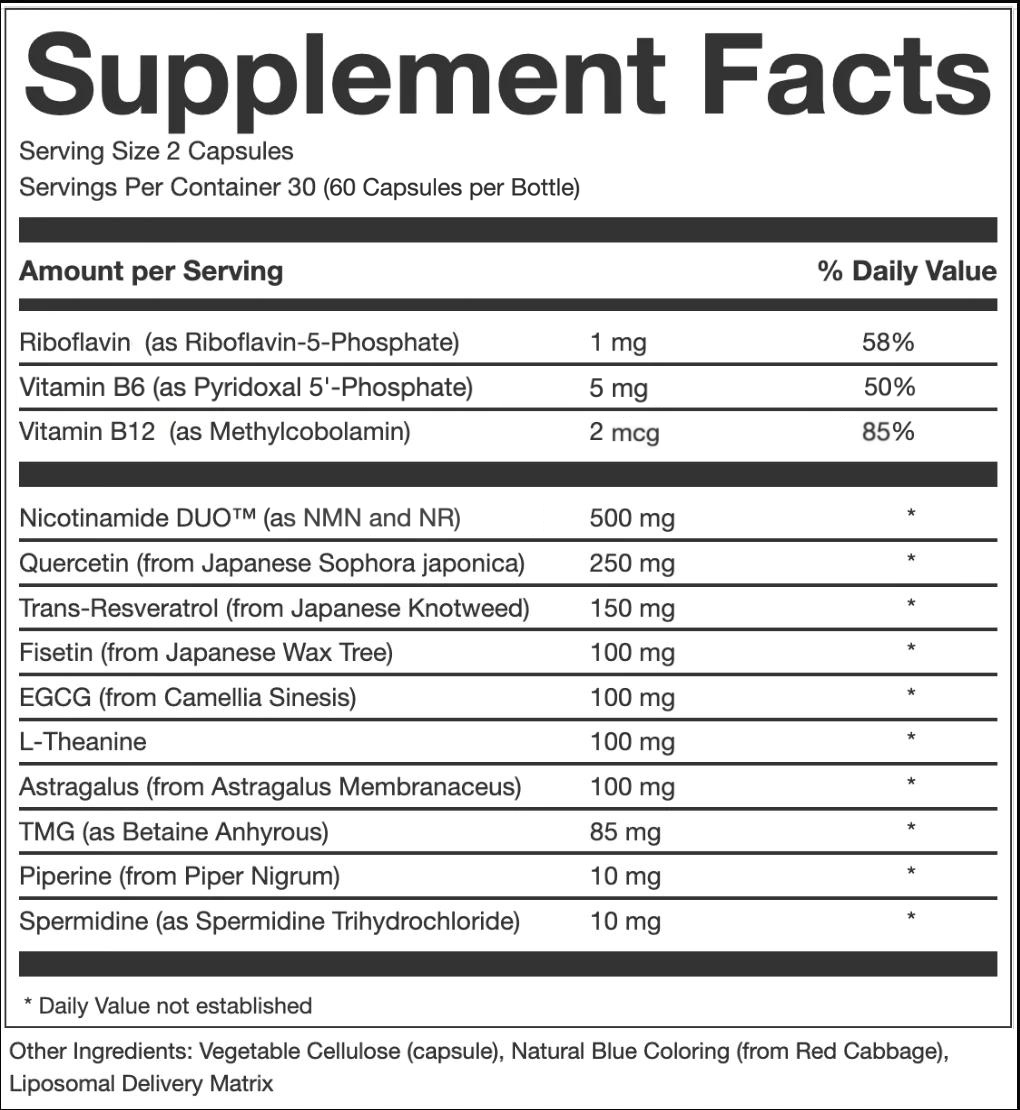
NICOTINAMIDE DUO:
Nicotinamide DUO™ (NMN, NAD+) has been shown to have a variety of benefits including:
✅ 1. Increased Energy and Reduced Fatigue:
NMN helps increase NAD+ levels, which are essential for mitochondrial energy production in cells.
This can lead to increased energy levels, reduced fatigue, and improved physical performance.
✅ 2. Improved Muscle Function and Strength:
NMN may help reverse age-related declines in muscle strength and size, which is called sarcopenia.
Studies have shown that NMN can improve muscle strength, endurance, and oxygen utilization in older adults and athletes.
✅ 3. Enhanced Cognitive Function:
Some research suggests that NMN may improve cognitive function and protect against age-related cognitive decline, including in models of Alzheimer's disease.
This could be due to NMN's ability to enhance energy metabolism in brain cells and reduce oxidative stress.
✅ 4. Protection Against Age-Related Decline:
NMN may help protect against various age-related declines, including those in the cardiovascular system, kidneys, liver, and other organs.
It can also help maintain the integrity of the blood-brain barrier, which is important for brain health.
✅ 5. Other Potential Benefits:
Improved Insulin Sensitivity:
NMN may improve insulin sensitivity, which is important for maintaining blood sugar levels and preventing conditions like type 2 diabetes.
Reduced Age-Associated Weight Gain:
NMN may help suppress age-related weight gain and improve body composition.
QUERCETIN:
Quercetin is a plant flavonoid found in many fruits, vegetables, and grains—especially onions, apples, and berries. It's widely used as a dietary supplement for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immune-supporting properties.
Here are the key potential benefits of taking quercetin:
✅ 1. Powerful Antioxidant
What it does: Neutralizes free radicals and reduces oxidative damage to cells and tissues.
Why it matters: Oxidative stress is linked to aging, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases.
✅ 2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Inhibits inflammatory enzymes and cytokines (like TNF-α, IL-6).
May help reduce symptoms of chronic inflammatory conditions such as arthritis or allergies.
✅ 3. Supports Immune Function
Enhances immune response while modulating excessive inflammation.
Studied for use in viral infections (e.g., colds, flu, even COVID-19 adjunctive therapy) due to antiviral and immune-balancing effects.
✅ 4. Allergy Relief
Acts as a natural antihistamine by stabilizing mast cells and reducing histamine release.
May help alleviate hay fever (allergic rhinitis) and seasonal allergies.
✅ 5. Heart Health
May reduce blood pressure, improve endothelial function, and lower LDL oxidation.
Helps relax blood vessels through nitric oxide modulation.
✅ 6. Blood Sugar Control
Improves insulin sensitivity and lowers blood glucose levels in some studies.
May be helpful for people with metabolic syndrome or type 2 diabetes.
✅ 7. Brain Health & Neuroprotection
May protect brain cells from oxidative damage and inflammation.
Early evidence suggests benefits for memory and cognitive decline.
✅ 8. Exercise Recovery
May reduce exercise-induced inflammation and oxidative stress, helping with muscle recovery and performance.
RESVERATROL:
Resveratrol is a natural polyphenol found in red grapes, wine, berries, and peanuts. It has gained attention for its potential health benefits, especially related to aging and chronic diseases.
Here's a summary of the main potential benefits of taking resveratrol:
✅ 1. Antioxidant Effects
What it does: Neutralizes free radicals that damage cells.
Why it matters: May reduce oxidative stress, a contributor to aging and disease.
✅ 2. Heart Health
Improves endothelial function: Helps arteries stay flexible and improves blood flow.
Reduces LDL cholesterol oxidation: May help prevent plaque buildup in arteries.
Mild blood pressure-lowering effects.
✅ 3. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Resveratrol may reduce markers of inflammation such as CRP and TNF-α, potentially beneficial for conditions like arthritis or metabolic syndrome.
✅ 4. May Support Brain Health
Neuroprotective effects: Animal studies suggest it may protect against cognitive decline by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain.
May enhance cerebral blood flow and potentially benefit memory.
✅ 5. Potential Anti-Aging Effects
Activates sirtuins (especially SIRT1), proteins associated with cellular health and longevity.
Mimics some effects of caloric restriction, which is linked to lifespan extension in various organisms.
✅ 6. Blood Sugar Regulation
May improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood glucose levels, especially in people with type 2 diabetes.
✅ 7. Anti-Cancer Potential
Laboratory studies show it may inhibit cancer cell growth and promote apoptosis (cell death) in some cancers, though human evidence is still limited.
FISETIN:
Fisetin is a naturally occurring flavonoid found in strawberries, apples, grapes, onions, and cucumbers. It's gaining attention for its unique role as a senolytic agent, meaning it helps clear out "senescent" cells—damaged cells that no longer divide and contribute to aging and disease.
Here are the main potential benefits of taking fisetin:
✅ 1. Senolytic Activity (Anti-Aging)
Clears senescent cells, which accumulate with age and promote inflammation and tissue damage.
May slow biological aging and improve tissue function in organs like the brain, liver, and kidneys (shown in animal studies).
One of the most promising natural compounds for healthy longevity support.
✅ 2. Brain and Cognitive Health
Crosses the blood-brain barrier and may protect against neurodegeneration.
Shown to improve memory and reduce cognitive decline in animal models of Alzheimer’s.
Reduces brain inflammation and oxidative stress.
✅ 3. Potent Antioxidant
Neutralizes free radicals and enhances glutathione levels, the body’s master antioxidant.
Helps protect cells and DNA from oxidative damage.
✅ 4. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokines (like IL-6, TNF-α).
May help manage chronic inflammatory conditions such as arthritis or metabolic syndrome.
✅ 5. Supports Metabolic and Cardiovascular Health
Improves insulin sensitivity and may lower blood sugar.
Potential to lower cholesterol and reduce arterial inflammation.
✅ 6. May Have Anti-Cancer Properties
In lab studies, fisetin has shown the ability to inhibit tumor growth, induce cancer cell death, and prevent metastasis.
Human studies are very limited but ongoing.
ASTRAGALUS:
Astragalus (Astragalus membranaceus) is a traditional Chinese herb used for thousands of years, known primarily for its immune-boosting, anti-aging, and adaptogenic properties. Modern research supports many of its traditional uses, especially in the context of immunity, inflammation, and longevity.
Here are the key benefits of taking astragalus:
✅ 1. Immune System Support
Stimulates white blood cell production, helping the body fight infections more effectively.
Enhances both innate and adaptive immunity.
May reduce the frequency and duration of colds and upper respiratory infections.
✅ 2. Anti-Aging & Longevity
Contains compounds that support telomere maintenance, especially cycloastragenol and astragaloside IV.
Telomeres protect DNA during cell division and their length is a biomarker of aging.
Used in longevity stacks for its potential to slow biological aging.
✅ 3. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Reduces levels of inflammatory markers (like TNF-α, IL-6).
Helpful for chronic inflammatory conditions like arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease.
✅ 4. Cardiovascular Health
May help lower blood pressure, improve circulation, and protect the heart muscle.
Shown to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in blood vessels.
Sometimes used alongside conventional treatments for heart failure.
✅ 5. Kidney Health
Protects against diabetic nephropathy and other forms of chronic kidney disease in some studies.
Reduces proteinuria and may improve overall kidney function (used widely in China as an adjunct therapy).
✅ 6. Adaptogenic & Anti-Stress Effects
Helps the body adapt to physical and emotional stress.
May improve resilience, reduce fatigue, and enhance energy levels without overstimulation.
✅ 7. Antioxidant Support
Rich in flavonoids, saponins, and polysaccharides that neutralize free radicals.
Protects cells and tissues from oxidative damage.
L-THEANINE:
L-theanine is a unique amino acid found almost exclusively in green tea. It’s widely used as a supplement for its calming and nootropic (brain-enhancing) effects—without sedation or drowsiness.
Here are the main benefits of taking L-theanine:
✅ 1. Promotes Relaxation Without Drowsiness
Increases alpha brain waves, associated with calm alertness and mental clarity.
Often used to reduce stress and anxiety without making you sleepy.
Helps “take the edge off” stimulants like caffeine.
✅ 2. Enhances Focus and Attention
Improves concentration and task switching, especially when taken with caffeine.
Common in nootropic stacks for productivity and studying.
✅ 3. Reduces Anxiety and Stress
Modulates neurotransmitters like GABA, dopamine, and serotonin, helping regulate mood and anxiety.
Shown in studies to reduce heart rate and cortisol during stressful situations.
✅ 4. Supports Better Sleep Quality
Helps you fall asleep more easily and improves sleep depth and quality.
Does not act like a sedative—more helpful for calming a busy mind before bed.
Often combined with magnesium or melatonin in sleep formulas.
✅ 5. May Protect Brain Health
Acts as a neuroprotective antioxidant, helping protect neurons from damage.
May support long-term cognitive health and reduce risk of age-related decline (limited human evidence so far).
✅ 6. Helps with Mood and Emotional Balance
Subtle mood-lifting effects, especially in people under stress or with mild anxiety.
May help reduce symptoms of depression when used alongside other treatments.
EGCG:
EGCG (Epigallocatechin gallate) is the most abundant and active catechin in green tea, known for its strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It's been widely studied for its effects on metabolism, heart health, brain function, and even cancer prevention.
Here are the key benefits of taking EGCG:
✅ 1. Powerful Antioxidant
Neutralizes free radicals and protects cells from oxidative damage.
Helps preserve DNA, lipids, and proteins from age-related deterioration.
✅ 2. Supports Weight Loss and Metabolism
Boosts thermogenesis and fat oxidation.
Often included in weight-loss supplements due to its mild metabolism-boosting effects.
May help reduce visceral fat (the type linked to metabolic disorders).
✅ 3. Cardiovascular Health
Lowers LDL cholesterol and triglycerides.
Improves endothelial function (blood vessel health).
Reduces blood pressure and arterial inflammation.
✅ 4. Brain Protection and Cognitive Support
May protect against neurodegeneration by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain.
Increases dopamine and acetylcholine levels, both important for mood and memory.
Linked to lower risk of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s in some population studies.
✅ 5. Anti-Cancer Properties
Inhibits the growth of various cancer cells in lab studies (e.g., breast, prostate, colon).
Suppresses angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels in tumors) and promotes apoptosis (cell death).
Human studies are still inconclusive but promising.
✅ 6. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Suppresses key inflammatory pathways (NF-κB, COX-2).
May help with chronic inflammation, including autoimmune conditions.
✅ 7. Blood Sugar and Insulin Regulation
May improve insulin sensitivity and reduce fasting blood glucose levels.
Potentially helpful for people with metabolic syndrome or type 2 diabetes.
TMG:
TMG (Trimethylglycine), also known as betaine, is a compound naturally found in beets, spinach, and whole grains. It plays a key role in methylation, liver health, and cellular function, and it's often used in longevity and performance supplementation.
Here are the primary benefits of taking TMG:
✅ 1. Supports Methylation (Homocysteine Reduction)
TMG donates methyl groups to convert homocysteine (a potentially harmful amino acid) into methionine.
Why it matters: High homocysteine is linked to heart disease, stroke, cognitive decline, and poor methylation status.
Often used alongside vitamin B12, B6, and folate to optimize methylation pathways.
✅ 2. Cardiovascular Protection
By lowering homocysteine, TMG may reduce the risk of atherosclerosis, blood clots, and cardiovascular events.
Supports the integrity and flexibility of blood vessels.
✅ 3. Liver Function Support
TMG helps metabolize fats in the liver and prevent fatty liver disease.
Often used in conditions like NAFLD (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) to improve lipid metabolism.
✅ 4. Athletic Performance & Muscle Strength
Supports creatine synthesis, which helps with muscle power and recovery.
May improve hydration and endurance during workouts by acting as an osmolyte (helps cells retain water).
✅ 5. Cellular Hydration & Stress Protection
As an osmoprotectant, TMG helps maintain cellular water balance and protects cells from stress-related damage.
Especially valuable during dehydration, heat stress, or oxidative stress.
✅ 6. Cognitive and Mood Support
Supports SAMe (S-adenosylmethionine) production, a key molecule in brain chemistry and mood regulation.
May assist with mental clarity, focus, and emotional stability, especially in people with methylation imbalances.
SPERMIDINE:
Spermidine is a naturally occurring polyamine found in foods like wheat germ, soybeans, mushrooms, and aged cheese. It's rapidly gaining attention for its anti-aging and cellular renewal properties—especially due to its ability to promote autophagy, a key process in longevity science.
Here are the main benefits of taking spermidine:
✅ 1. Activates Autophagy (Cellular Cleanup)
Autophagy is the process by which cells break down and recycle damaged components.
Spermidine mimics the effects of caloric restriction or fasting, triggering autophagy without food deprivation.
Helps maintain cellular health and function as you age.
✅ 2. Anti-Aging and Longevity
Linked to increased lifespan in yeast, flies, mice, and potentially humans.
May slow age-related decline by reducing cellular waste, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction.
✅ 3. Supports Brain Health
Promotes neuroprotection by reducing oxidative stress and enhancing autophagy in brain cells.
Associated with better memory and cognitive performance, especially in aging adults.
✅ 4. Cardiovascular Protection
May improve arterial elasticity, reduce blood pressure, and support heart cell health.
Higher spermidine intake is linked to lower cardiovascular mortality in observational studies.
✅ 5. Enhances Mitochondrial Function
Improves the quality control of mitochondria, which boosts cellular energy production and resilience to stress.
✅ 6. Supports Immune Function
Maintains the youthfulness of immune cells (particularly T cells) by helping them remove damaged proteins and organelles.
✅ 7. Skin and Hair Health
By promoting cellular renewal, spermidine may support healthier skin and hair, with some evidence suggesting benefits for hair growth cycles.
PIPERINE:
Piperine is the active compound in black pepper that gives it its pungent flavor—but more importantly, it's widely used in supplements for its ability to enhance nutrient absorption and provide anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
Here are the main benefits of taking piperine:
✅ 1. Dramatically Enhances Nutrient Absorption
Most well-known benefit.
Increases the bioavailability of various nutrients and compounds, such as:
Curcumin (by up to 2000%)
Resveratrol
EGCG
CoQ10, selenium, B vitamins, and more
Does this by slowing metabolism in the liver (inhibits CYP450 enzymes) and increasing intestinal absorption.
✅ 2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Reduces production of inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and TNF-α.
May help with joint pain, chronic inflammation, and even neuroinflammation.
✅ 3. Antioxidant Support
Neutralizes free radicals and reduces oxidative stress in tissues.
May protect cells from DNA damage and lipid peroxidation.
✅ 4. Brain Health & Neuroprotection
Shown in some studies to improve cognitive function and memory, particularly when combined with curcumin.
May increase serotonin and dopamine levels in the brain, with potential mood benefits.
✅ 5. Metabolism and Weight Management
May stimulate thermogenesis and fat metabolism.
Often included in fat-burning supplements for its mild metabolic boost.
Bundle Purchase Options:
Share








AEON Longevity Complex is a synergistic blend of 11 longevity ingredients that target the damages of aging.

The Ultimate Evolution in Longevity.
Perpetua Life Biotech is a U.S. based research and development company specializing in life extension and gerontology.
We're a dedicated group of professionals that have made it our life's mission to ensure you can live a longer and healthier life.
A recent study has shown boosting your NAD+ levels, and supplementing your diet with senolytic compounds like Resveratrol, Fisetin, and Quercetin may reverse age-related decline, and extend human lifespan.
AEON combines NAD+ precursors like NMИ and NR, with Resveratrol, Quercetin, Fisetin, AND 6 other age defying compounds in one affordable product!
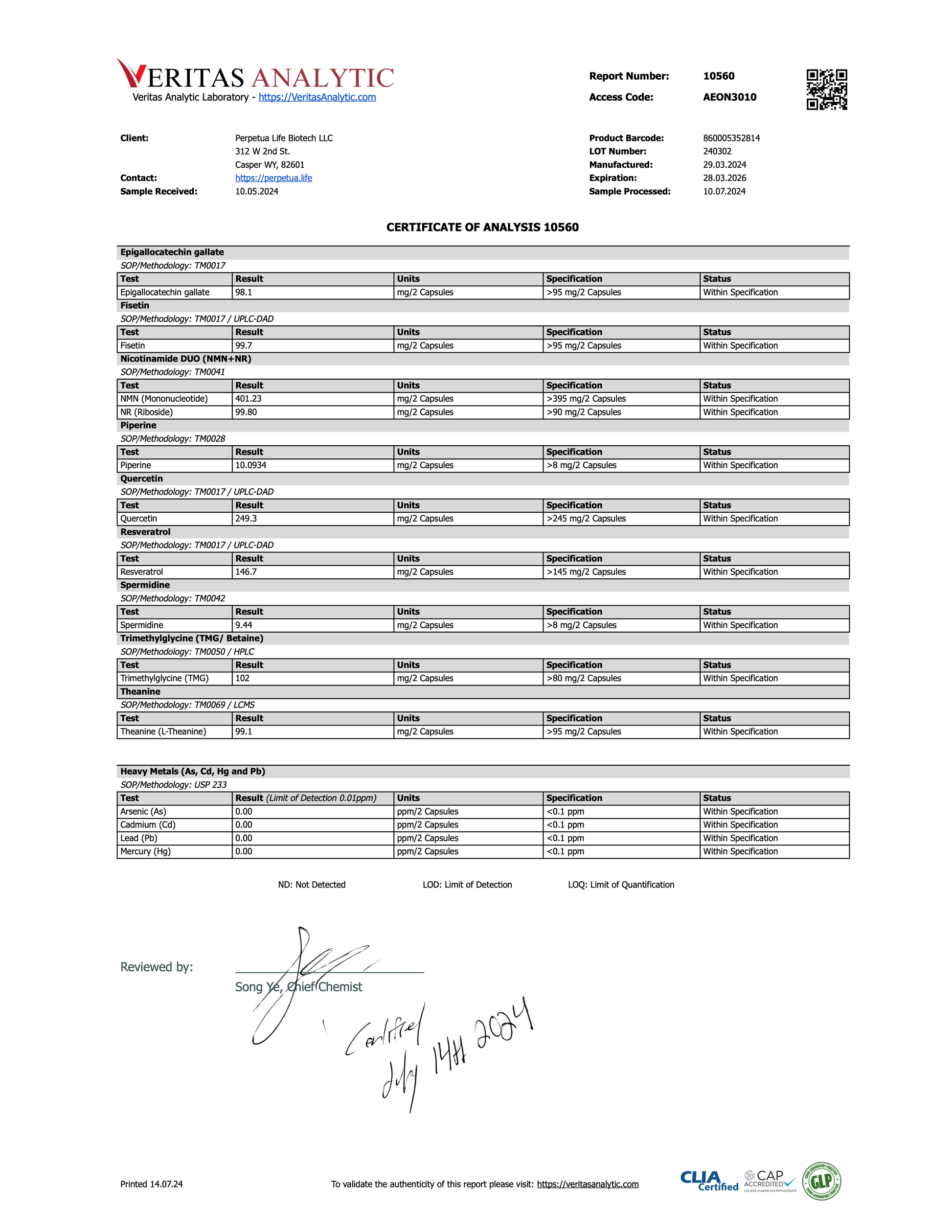
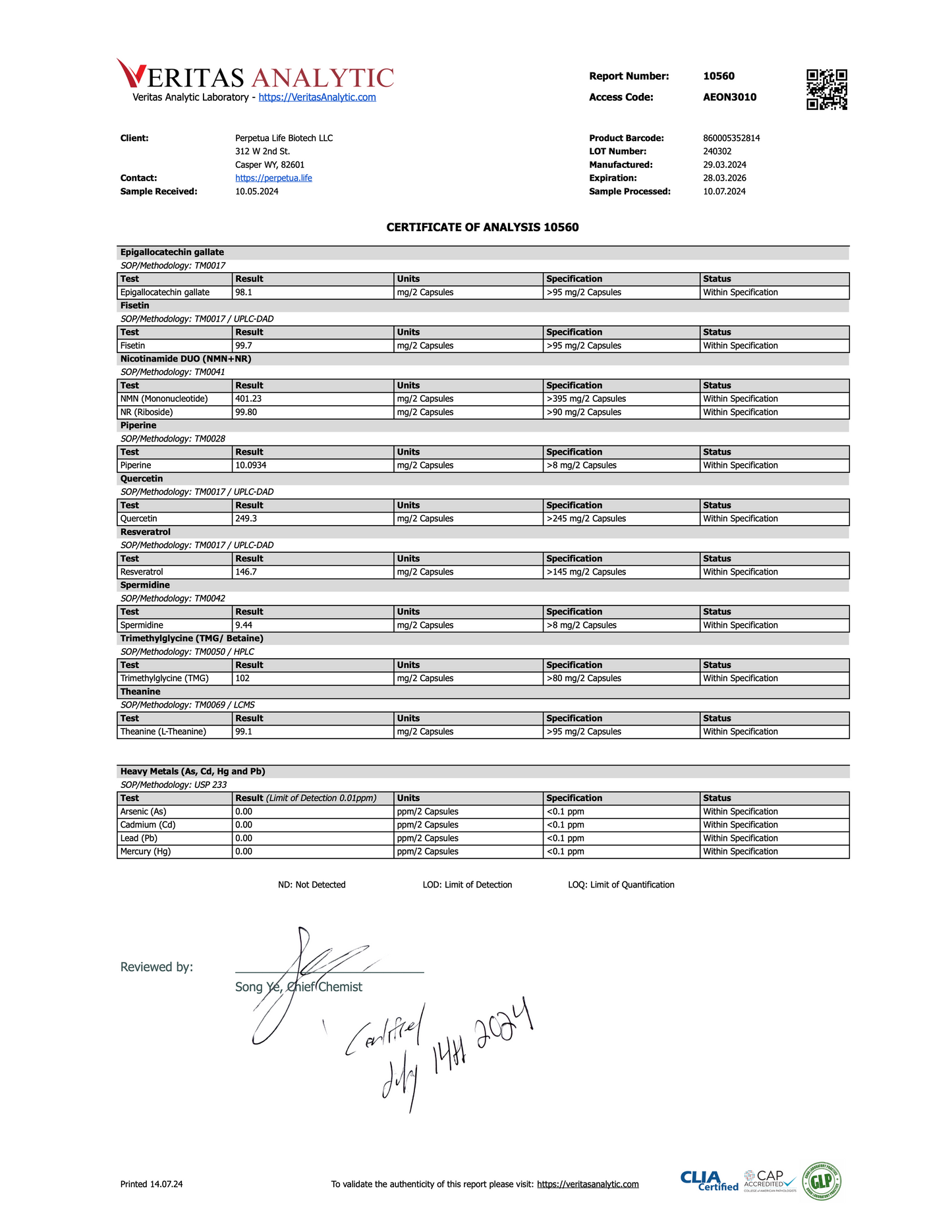
We're one of the very few companies who also regularly 3rd party test our products for Heavy Metal contaminants like Lead, Mercury, Cadmium, and Arsenic to make sure you get a safe, and effective product each and every time!
You can view the results HERE.
FAQ:
When and How should I take AEON Black?
For best absorption we advise taking 2 capsules of AEON Black a day with a meal. The bottle includes 60 capsules so it should last a full month.
What makes AEON better than other brands?
AEON combines more longevity ingredients than any other product into one easy to swallow pill. The formula is inspired by Dr. Sinclair's research and his book "Lifespan."
We also test our product for heavy metals which is something a lot of other companies don't do because they source their ingredients from countries like China where those levels are very high.
What are your subscription terms?
You can cancel your subscription at any time by using the link "manage subscription" at the top & bottom of this page. Alternatively, you can send us an email at support@perpetua.life and we will be happy to cancel it for you.
What are the main benefits of taking AEON?
AEON Longevity Complex is your all-in-one solution, replacing the need for 11+ supplements, targeting eight key areas of health: Energy, Immunity, Cognitive Function, Digestion, Cardiovascular Health, Hydration, Nourishment, and Cellular Renewal.
AEON makes it easier to live a healthier, more vibrant life.
Does AEON interact with any other medications?
AEON is vegan, non-gmo, and free from gluten, dairy, soy, and peanuts.
We've designed our product to be taken by individuals of all ages, and walks of life, including those taking blood thinners, statins, ACE inhibitors, and ARBs
How long until I start noticing results?
Users have reported everything from grey hair turning back to its original color, skin looking more vibrant, better sleep, more energy, and an overall improved sense of wellbeing within 2-3 months of consistent use.

AEON Black & White Bundle
Looking to take your longevity stack to the next level? Then the AEON Black & White Bundle is for you!